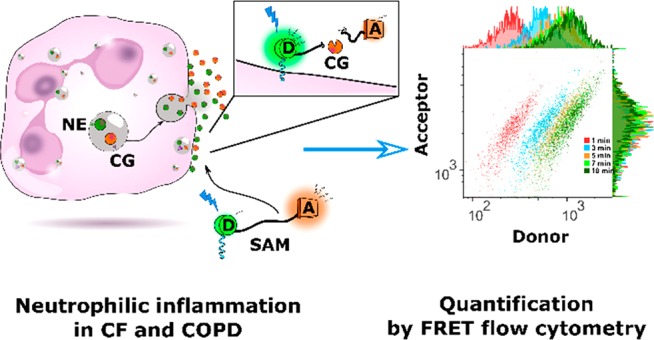
Muco-obstructive lung ailments function intensive bronchiectasis because of the uncontrolled launch of neutrophil serine proteases into the airways.
To assess if cathepsin G (CG) is a novel key participant in persistent lung irritation, we developed membrane-bound (mSAM) and soluble (sSAM) FRET reporters. The probes quantitatively revealed elevated CG exercise in samples from 46 sufferers.
For future fundamental science and personalised medical purposes, we developed a speedy, extremely informative, and simply translatable small-molecule FRET stream cytometry assay for monitoring protease exercise together with cathepsin G.
We demonstrated that mSAM distinguished wholesome from affected person cells by FRET-based stream cytometry with wonderful correlation to confocal microscopy information.
Imaging stream cytometry and confocal microscopy-based examination of F-actin and phosphoinositide dynamics throughout leukocyte immune-type receptor-mediated phagocytic occasions.
Cells of the innate immune system quickly detect and remove invading microbes utilizing surface-expressed immunoregulatory receptors that translate extracellular binding occasions into potent effector responses.
Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) leukocyte immune-type receptors (IpLITRs) are a household of immunoregulatory proteins which were proven to manage a number of innate immune cell effector responses together with the phagocytic course of.
The mechanisms by which these receptors regulate phagocytosis aren’t solely understood however now we have beforehand proven that completely different IpLITR-types use ITAM-dependent as nicely as ITAM-independent pathways for controlling goal engulfment.
The important goal of this research was to develop and use imaging stream cytometry and confocal microscopy-based assays to additional look at each F-actin and phosphoinositide dynamics that happen throughout the completely different IpLITR-mediated phagocytic pathways. Results present that the ITAM-dependent IpLITR-induced phagocytic response promotes canonical adjustments in F-actin polymerization and PI(4,5)P2 redistributions.
However, the ITAM-independent IpLITR phagocytic response induced distinctive patterns of F-actin and PI(4,5)P2 redistributions, that are seemingly as a consequence of its capability to manage different signaling pathways.
Additionally, each IpLITR-induced phagocytic pathways induced goal internalization into PI(3)P-enriched phagosomes indicative of a maturing phagosome compartment. Overall, this imaging-based platform will be additional utilized to observe the recruitment and distribution of signaling molecules throughout IpLITR-mediated phagocytic processes and might serve as a helpful technique for useful examinations of different immunoregulatory receptor-types in fish.